Huge Uk review examines affect of Delta variant on viral burden and vaccine efficiency
Scientists believe the most critical software to comprise the ongoing coronavirus sickness 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic is speedy vaccination. The pandemic has been triggered by the speedy transmission of significant acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-2 (SARS-CoV-2). Numerous research have been carried out to assess the usefulness of current COVID-19 vaccines in the normal populace. Some of these experiments have noted the superior effectiveness of the BNT162b2 vaccine produced by Pfizer-BioNTech and the ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 vaccine by Oxford-AstraZeneca, towards the Alpha (B.1.1.7) and previous variants.
Owing to mutations, there has been a continuous emergence of SARS-CoV-2 variants, which have threatened the effectiveness of the vaccines. In vitro reports have indicated a lowered neutralization exercise of vaccine-induced antibodies from some of the SARS-CoV-2 variants, e.g., Delta variant (B.1.617.2). This variant has brought on a surge in the selection of COVID-19 scenarios in numerous nations across the world, like these with substantial vaccination coverage, these types of as the British isles. Due to the higher infectiousness of the Delta variant, it has been labeled as a Variant of Concern (VoC).
Vaccine Success and the Delta Variant
Experts have pointed out the shortage of actual-time proof on the usefulness of the obtainable vaccines against the Delta variant. A current examine that employed info from the English symptomatic testing software exposed that the efficacy of a single dose of BNT162b2 or ChAdOx1 vaccine was significantly decrease towards symptomatic infection with the Delta variant than the Alpha variant. However, the two the vaccines ended up discovered to be productive from the Delta variant, with a insignificant reduction in efficacy, just after completion of the two-dose regime.
One more review performed in Scotland indicated lessened performance of vaccines in opposition to the Delta variant, even just after administering two doses of the vaccines. This examine also showed the superior efficacy of the vaccines against the Alpha variant. The effects of vaccination on clinic admission was not claimed.
A New Research
Now, a new examine released on the medRxiv* preprint server focused on figuring out the efficiency of the BNT162b2, ChAdOx1, and mRNA-1273 vaccines by conducting SARS-CoV-2 PCR-constructive checks. This research employed an considerable neighborhood-centered study (Workplace for National Data COVID-19 Infection Survey) of men and women residing in randomly picked personal homes across the Uk. Irrespective of signs and symptoms, vaccination, and prior bacterial infections, RT-PCR checks were done in these households on a pre-established routine.
Scientists identified the effectiveness of the vaccines based on total RT-PCR positivity, self-documented symptoms, and the cycle threshold (Ct) benefit that indicated the viral load. This review was carried out in two phases, and the initial stage was involving 1 December 2020 (commencement of vaccination program) and 16 Could 2021, for the duration of which period of time the Alpha variant was dominant.
The 2nd stage was from 17 May perhaps 2021 to 1 August 2021, when the Delta variant was dominant. Researchers also decided the variation in vaccine usefulness by very long-expression health ailments among the two age groups, i.e., 18-34 many years and 35-65 years. Also, vaccine efficacy was assessed dependent on the interval between initial and 2nd vaccination and prior an infection. Eventually, the viral load, applying Ct values, was assessed among freshly contaminated folks who became PCR-favourable following 14 days of obtaining the 2nd vaccine dose.
Principal Findings
This review reported that the effectiveness of the BNT162b2 and ChAd0x1 vaccines from the Delta variant was reduced as opposed to other SARS-CoV-2 variants, these as the Alpha pressure. Scientists identified that a one dose of the mRNA-1273 vaccine experienced comparable or far better usefulness than a solitary dose of the BNT162b2 or ChAdOx1 vaccine. The efficiency of two doses was comparable to the immune defense brought on following natural SARS-CoV-2 an infection.
The degree of immune responses induced by the BNT162b2 and ChAdOx1 vaccines differed considerably. Both of those the vaccines were observed to be remarkably efficient versus the new PCR positives, but a decrease in safety was noticed when the viral load was superior, in particular, in the case of the BNT162b2 vaccine.
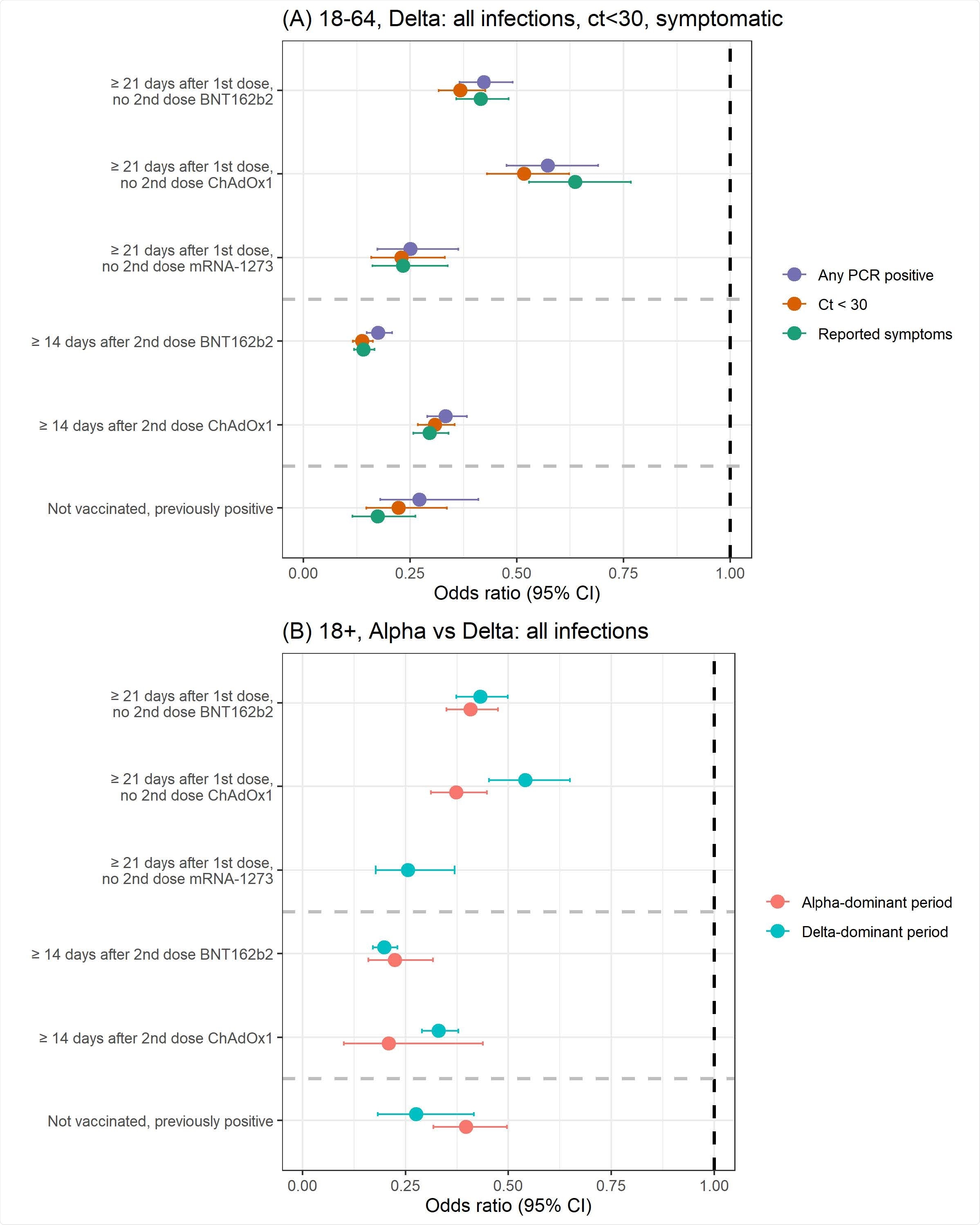
(A) Security towards all new PCR-constructive episodes, those with Ct<30, or with self-reported symptoms in those 18-64 years in the Delta-dominant period (B) Protection against all new PCR-positive episodes in those 18+ years in both the Alpha- and Delta-dominant period.
In the context of vaccine effectiveness with varied dose intervals, researchers found no significant variation in vaccine effectiveness. However, COVID-19 convalescent individuals who were vaccinated were found to possess greater immune protection compared to vaccinated individuals without a history of SARS-CoV-2 infection.
Surprisingly, individuals who completed the two doses of vaccine regime and were infected with the Delta variant exhibited a viral load comparable to those who were not vaccinated and were infected with this strain.
Conclusion
The main strength of this study is its sample size and design. Additionally, researchers accounted for the risk factors that influence vaccination. Some of the factors considered in this study are commonly documented in electronic health records, e.g., the long-term health conditions of a patient. However, most of the studies solely rely on the data available in the electronic databases, which may miss small intrinsic details. The current study incorporated data beyond what is available in these databases. One of the limitations of this study is that even though it has included numerous potential confounders, it might have excluded unknown confounders or misclassified a prior infection status. This might bring about a biased result.
The authors of this study stated that even though SARS-CoV-2 vaccination reduces new infections, the effectiveness in lowering the viral load against the Delta strain was found to be reduced.
*Important Notice
medRxiv publishes preliminary scientific reports that are not peer-reviewed and, therefore, should not be regarded as conclusive, guide clinical practice/health-related behavior, or treated as established information.

